MCV4U COURSE OUTLINE
Course Title: Calculus & Vectors
Grade: 12
Ministry Course Code: MCV4U
Course Type: University
Credit Value: 1.00
Course Hours: 110
Department: Mathematics
Revision Date: N/A
Policy Document: Mathematics, The Ontario Curriculum, Grades 11 and 12, 2007 (Revised)
http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/curriculum/secondary/math1112currb.pdf

Domestic Student Price: $550
International Student Price: $799
COURSE DESCRIPTION
This course builds on students’ previous experience with functions and their developing understanding of rates of change. Students will solve problems involving geometric and algebraic representations of vectors and representations of lines and planes in three-dimensional space; broaden their understanding of rates of change to include the derivatives of polynomial, sinusoidal, exponential, rational, and radical functions; and apply these concepts and skills to the modelling of real-world relationships. Students will also refine their use of the mathematical processes necessary for success in senior mathematics. This course is intended for students who choose to pursue careers in fields such as science, engineering, economics, and some areas of business, including those students who will be required to take a university-level calculus, linear algebra, or physics course.
OVERALL EXPECTATIONS
Rate of Change
By the end of this course, students will:
demonstrate an understanding of rate of change by making connections between average rate of change over an interval and instantaneous rate of change at a point, using the slopes of secants and tangents and the concept of the limit;
graph the derivatives of polynomial, sinusoidal, and exponential functions, and make connections between the numeric, graphical, and algebraic representations of a function and its derivative;
verify graphically and algebraically the rules for determining derivatives; apply these rules to determine the derivatives of polynomial, sinusoidal, exponential, rational, and radical functions, and simple combinations of functions; and solve related problems.
Derivatives & Their Applications
By the end of this course, students will:
1. solve problems, including optimization problems, that require the use of the concepts and procedures associated with the derivative, including problems arising from real-world applications and involving the development of mathematical models.
2. verify graphically and algebraically the rules for determining derivatives; apply these rules to determine the derivatives of polynomial, sinusoidal, exponential, rational, and radical functions, and simple combinations of functions; and solve related problems.
Curve Sketching and Optimization
By the end of this course, students will:
make connections, graphically and algebraically, between the key features of a function and its first and second derivatives, and use the connections in curve sketching;
solve problems, including optimization problems, that require the use of the concepts and procedures associated with the derivative, including problems arising from real-world applications and involving the development of mathematical models.
Geometry & Algebra of Vectors
By the end of this course, students will:
demonstrate an understanding of vectors in two-space and three-space by representing them algebraically and geometrically and by recognizing their applications;
perform operations on vectors in two-space and three-space, and use the properties of these operations to solve problems, including those arising from real-world applications;
distinguish between the geometric representations of a single linear equation or a system of two linear equations in two-space and three-space, and determine different geometric configurations of lines and planes in three-space;
represent lines and planes using scalar, vector, and parametric equations, and solve problems involving distances and intersections.
OUTLINE OF COURSE CONTENT
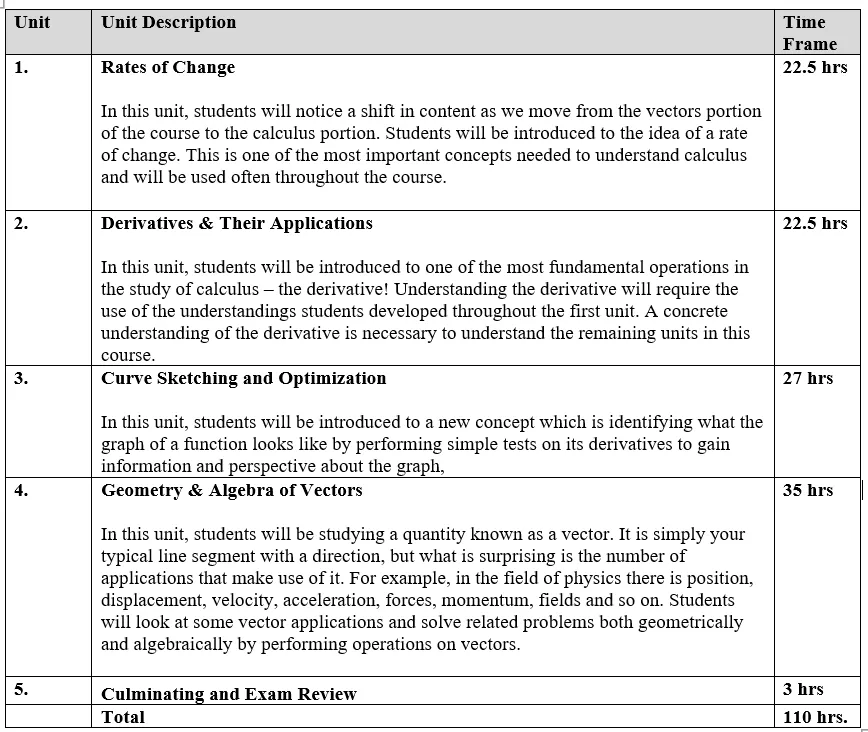
TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used to allow students many opportunities to attain the necessary skills for success in this course and in future studies. In all activities, consideration will be taken to ensure that individual students’ multiple intelligences and learning strengths are addressed through the use of varied and multiple activities in each lesson.
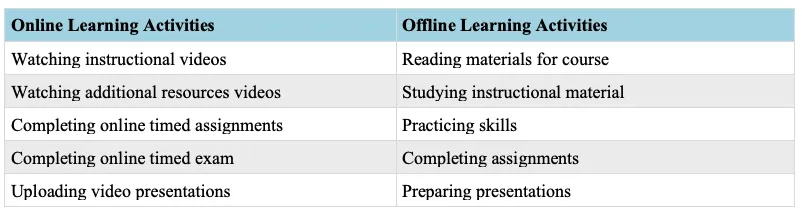
STRATEGIES FOR ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION OF STUDENT PERFORMANCE
The primary purpose of assessment and evaluation is to improve student learning. Assessment and evaluation is based on the Ministry of Education’s Growing Success policy document, which articulates the Ministry’s vision for how assessment and evaluation is practiced in Ontario schools.
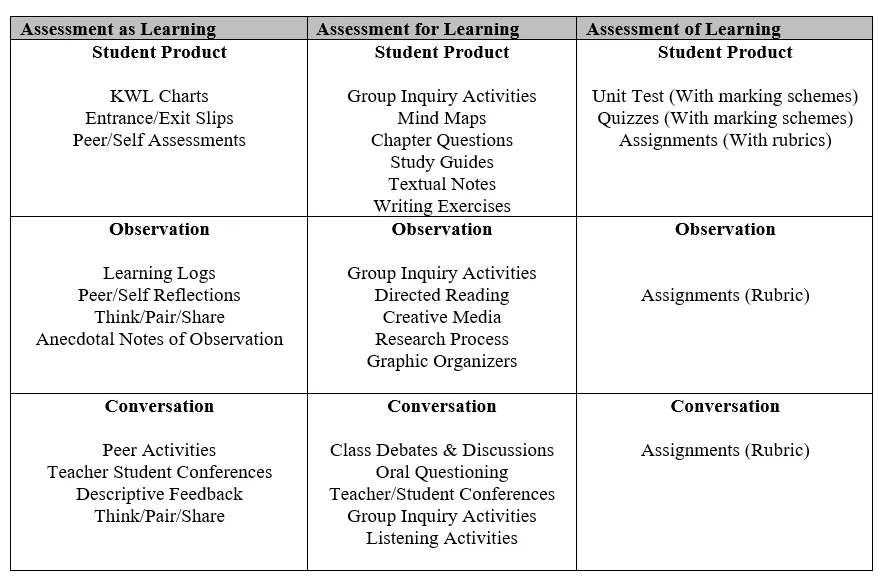
Growing Success describes the three assessment types as follows:
Assessment as Learning: focuses on the explicit fostering of students’ capacity over time to be their own best assessors, but teachers need to start by presenting and modelling external, structured opportunities for students to assess themselves.
Assessment for Learning: the process of seeking and interpreting evidence for use by learners and their teachers to decide where the learners are in their learning, where they need to go, and how best to get there.
Assessment of Learning: the assessment that becomes public and results in statements or symbols about how well students are learning.
ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION
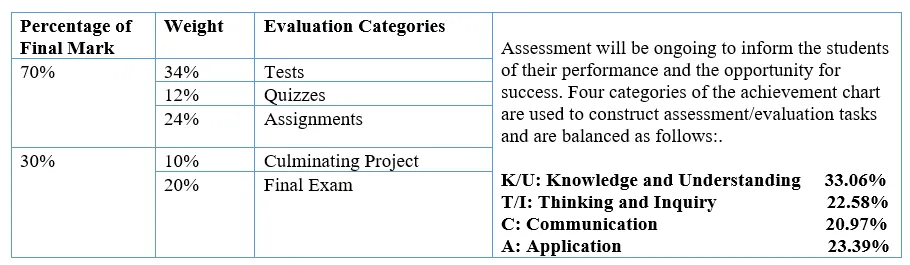
EVALUATION SCHEME
A final grade (percentage mark) is calculated at the end of the course and reflects the quality of the student’s achievement of the overall expectations of the course, in accordance with the provincial curriculum.
The final grade will be determined as follows:
Seventy percent (70%) of the grade will be based on evaluation conducted throughout the course. This portion of the grade should reflect the student’s most consistent level of achievement throughout the course, although special consideration should be given to more recent evidence of achievement.
Thirty percent (30%) of the grade will be based on a final evaluation administered at or towards the end of the course. This evaluation will be based on evidence from one or a combination of the following: an examination, a performance, an essay, and/or another method of evaluation suitable to the course content. The final evaluation allows the student an opportunity to demonstrate comprehensive achievement of the overall expectations for the course.
PLAGIARISM
Plagiarism is a serious offense. It is defined as taking words, phrasing, sentence structure, or any other element of the expression of another person’s ideas, and using them as if they were your own. Plagiarism is a violation of another person’s rights, whether the material taken is great or small.Students will be assisted in developing strategies and techniques to avoid plagiarism. They need to be aware that plagiarized term work will be penalized and could result in a mark of zero.
NEW!
SBI3U
SCH4U
ENG4U
ENG3U
SBI4U
MDM4U
MCR3U
BBB4M
BOH4M
MHF4U
We offer a hybrid model of education for all of our online courses, you can earn your OSSD with us!
How We Help Students

Complete Prerequisites
as you work toward your Ontario Secondary School Diploma

Earn
as you work toward your Ontario Secondary School Diploma

Retake
a course you had trouble with

Meet
a course you had trouble with

Take
a course not offered
In your home school

Trust
a course not offered
In your home school
Spark Asher Academy Alumni University Destinations






